
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer just a concept from science fiction—it’s part of everyday life. From recommendation engines on Netflix to virtual assistants like Siri or ChatGPT, AI is transforming the way we work, learn, and interact with technology. Yet for many beginners, AI can seem complex and intimidating. This guide breaks down the basics, explaining AI in simple terms, with real-world examples and insights into how it works.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
At its core, AI is the ability of a machine or system to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence. These tasks can include:
- Learning from data (like recognizing patterns)
- Understanding language
- Making decisions
- Solving problems
- Generating content (text, images, videos)
AI is essentially computer programs that mimic certain human thinking processes, often using advanced mathematics and algorithms to “learn” from experience.
Example:
When you type a question into Google or ChatGPT, AI analyzes millions of examples and patterns in data to generate a response that makes sense. That’s AI in action.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
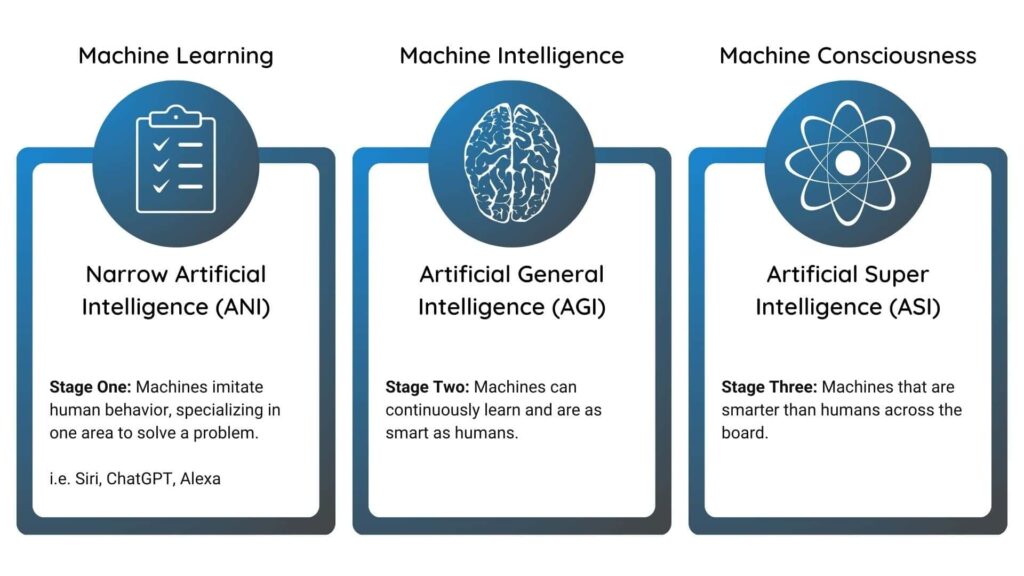
AI is not a single technology—it comes in several forms, ranging from simple automation to advanced reasoning.
- Narrow AI (Weak AI)
- Designed for a specific task
- Most AI today is narrow AI
- Examples:
- Spam filters in your email
- Voice assistants like Alexa
- Netflix or Spotify recommendation systems
- General AI (Strong AI)
- Hypothetical AI that can perform any task a human can do
- Can reason, understand, and adapt across different areas
- Examples: Currently does not exist
- Superintelligent AI
- AI that surpasses human intelligence
- Theoretical concept often discussed in ethics and philosophy
- Examples: Seen in science fiction, like AI characters in movies such as Her or Ex Machina
How AI Works: The Basics
AI systems rely on three main processes:
- Data Collection
AI learns from examples, often huge datasets. The more data, the better it can recognize patterns. Example: A self-driving car uses data from cameras and sensors to understand road conditions and traffic. - Learning and Training
AI uses algorithms to identify patterns in data. This is often called machine learning (ML). Example: Email spam filters are trained on thousands of emails labeled as “spam” or “not spam,” learning to predict which emails to block. - Prediction and Decision-Making
Once trained, AI makes predictions or decisions based on new data. Example: Predictive text on your smartphone suggests the next word while you type based on what it has learned from previous sentences.
Popular AI Technologies
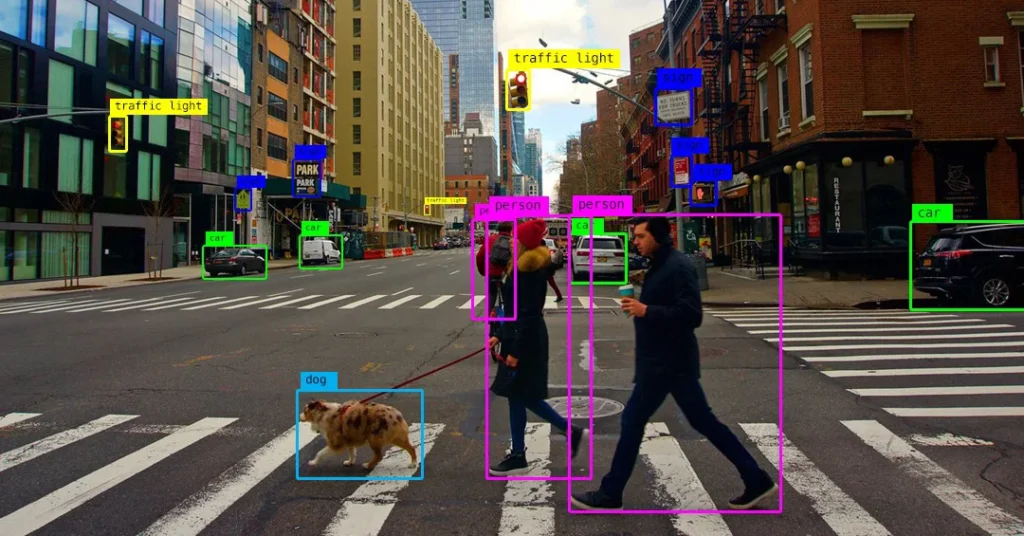
AI is not a single tool—it is a collection of technologies. Here are some common types:
- Machine Learning (ML): AI systems learn from historical data to make predictions.
Example: Stock market forecasting tools. - Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI understands and generates human language.
Example: ChatGPT or Google Translate. - Computer Vision: AI interprets images or video.
Example: Facial recognition or self-driving cars. - Robotics: Machines powered by AI can perform physical tasks.
Example: Warehouse robots like those used by Amazon. - Generative AI: AI creates content such as text, images, music, or code.
Example: DALL·E generates images from text prompts; ChatGPT generates written content.
Real-World Examples of AI
AI is already embedded in everyday life. Some examples include:
- Healthcare: AI analyzes medical images to detect diseases like cancer early.
- Finance: Fraud detection systems identify suspicious transactions in real time.
- Entertainment: Streaming platforms recommend shows based on your viewing habits.
- Transportation: AI powers self-driving cars, navigation apps, and traffic optimization.
- Customer Service: Chatbots answer common questions on websites.
These examples show how AI can save time, improve decisions, and make processes more efficient.
Benefits of AI
- Efficiency: Automates repetitive tasks, freeing human time.
- Accuracy: Reduces errors in tasks like medical diagnosis or financial analysis.
- Personalization: Provides tailored recommendations, learning from individual behavior.
- Innovation: Opens opportunities for new products, services, and discoveries.
Challenges and Risks of AI
While AI has enormous potential, it also comes with challenges:
- Bias in AI: AI can inherit biases from the data it’s trained on, leading to unfair outcomes.
Example: A hiring algorithm may favor certain demographics if historical hiring data is biased. - Privacy Concerns: AI systems often use personal data, raising privacy issues.
- Job Displacement: Automation may replace some jobs, particularly repetitive or routine roles.
- Misuse: AI can generate fake content or be used unethically.
Understanding these risks is important for using AI responsibly.
Tips for Beginners Learning AI
- Start with AI in Everyday Life: Explore chatbots, virtual assistants, and recommendation systems.
- Learn Basic Concepts: Understand machine learning, natural language processing, and data analysis.
- Experiment with Tools: Try beginner-friendly AI platforms like ChatGPT, Canva AI, or AI image generators.
- Take Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, or Khan Academy offer introductory AI courses.
- Stay Curious: AI is evolving rapidly; read blogs, watch tutorials, and follow industry news.
The Future of AI

AI is expected to become increasingly integrated into our daily lives. Future developments may include:
- Smarter virtual assistants that understand context better
- AI-driven healthcare with early disease detection and personalized treatment
- Improved autonomous vehicles and transportation systems
- Creative AI that generates art, music, and literature
While the possibilities are exciting, it’s important to balance innovation with ethics and responsibility. AI should enhance human life, not replace human judgment entirely.
Final Thoughts
Artificial Intelligence might seem intimidating at first, but at its core, it’s about creating systems that can learn, reason, and perform tasks intelligently. From voice assistants to self-driving cars, AI is already shaping our world—and understanding the basics empowers you to interact with it effectively.
Start small, explore AI tools, learn the fundamental concepts, and stay informed about ethical considerations. With time, you’ll gain a clear understanding of AI’s potential and its practical applications in everyday life.

