
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s a practical tool that businesses of all sizes can leverage to improve efficiency, productivity, and customer experience. From automating repetitive tasks to analyzing data for strategic insights, AI tools offer transformative potential.
However, integrating AI effectively is more than just installing software. It requires strategy, planning, and careful execution to ensure the tools provide real value without disrupting existing workflows. This guide explores how businesses can adopt AI successfully, with examples and best practices.
1. Identify the Right Use Cases

The first step in effective AI integration is identifying where AI can have the greatest impact. Not every process benefits equally from automation or AI assistance. Businesses should focus on areas that are repetitive, data-intensive, or decision-driven.
Examples of high-impact AI use cases:
- Customer Support: AI chatbots handle common queries, freeing human agents for complex cases.
- Sales and Marketing: Predictive analytics can identify leads most likely to convert.
- Operations: AI-powered scheduling or inventory management improves efficiency.
- Finance: AI detects fraud patterns and automates invoice processing.
Tip: Conduct an internal audit to pinpoint tasks that are time-consuming, error-prone, or data-heavy—these are often ideal for AI adoption.
2. Choose the Right AI Tools
Once you know your use cases, the next step is selecting AI tools that fit your business needs. The AI landscape is vast, ranging from specialized platforms to all-in-one solutions.
Categories and examples:
- AI Customer Support: Intercom, Drift, or Zendesk AI
- AI Analytics & Insights: Tableau AI, Microsoft Power BI with AI features
- AI for Productivity: Notion AI, Microsoft Copilot, or Grammarly Business
- AI for Marketing: HubSpot AI, Jasper, or Phrasee for copy generation
Tip: Look for tools that integrate with your existing software stack. Seamless integration reduces disruption and accelerates adoption.
3. Start Small with Pilot Projects
Jumping straight into enterprise-wide AI adoption can backfire. Instead, start with pilot projects that are low-risk but high-visibility.
How to run a pilot:
- Select a single department or process
- Define clear goals and metrics
- Train relevant staff on the tool
- Monitor results and gather feedback
Example:
A retail business might pilot an AI chatbot to handle online customer queries. If it reduces response times and improves satisfaction, the solution can then be rolled out to other channels.
4. Train Employees and Build AI Literacy

AI tools are only effective if employees understand how to use them. Training and change management are critical.
Training tips:
- Provide role-specific tutorials and workshops
- Explain how AI complements, not replaces, human work
- Encourage experimentation in a safe environment
Example:
Sales teams using predictive analytics should learn how to interpret AI-generated leads and combine insights with human judgment for closing deals.
5. Integrate AI into Existing Workflows
AI adoption fails when tools exist in isolation. Successful integration means embedding AI into daily workflows and processes.
How to integrate effectively:
- Connect AI tools with CRM, ERP, or project management systems
- Automate repetitive tasks like data entry or report generation
- Use AI to augment decision-making rather than replace it entirely
Example:
A marketing team could integrate an AI content generator into its editorial calendar, automatically suggesting blog ideas based on trending topics while editors review and refine the output.
6. Monitor Performance and Measure ROI
AI adoption should be data-driven. Define metrics to evaluate whether the AI tool is delivering value.
Key performance indicators (KPIs):
- Time saved on repetitive tasks
- Increase in sales or customer engagement
- Accuracy improvements in forecasting or reporting
- Employee satisfaction with AI assistance
Example:
A logistics company implementing AI-powered route optimization can track delivery times and fuel costs before and after AI adoption to measure ROI.
7. Maintain Data Quality and Privacy
AI relies on data, so clean, accurate, and secure data is essential for effective results.
Best practices:
- Standardize data formats and ensure completeness
- Implement strong privacy measures and comply with regulations (e.g., GDPR)
- Regularly audit AI outputs for accuracy and bias
Example:
A financial firm using AI to detect fraud must ensure transaction data is accurate and up to date, or the AI might flag false positives or miss genuine threats.
8. Choose the Right Level of AI Automation
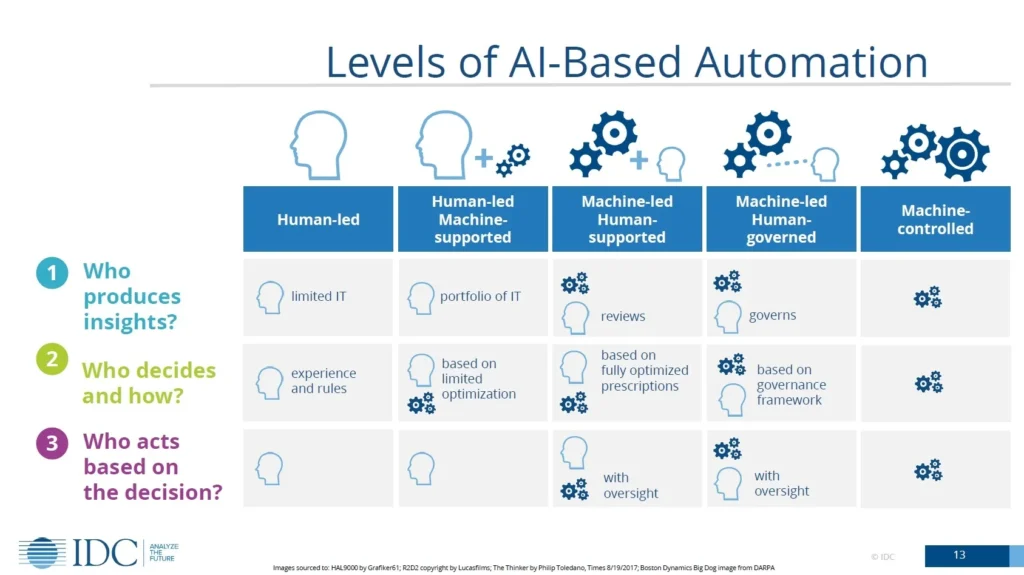
Not every task should be fully automated. Evaluate where human oversight is necessary and where automation is safe.
Examples:
- Automate: Invoice processing, basic customer queries, social media posting
- Human + AI: Sales decision-making, hiring recommendations, legal contract review
Tip: Start with AI handling low-risk tasks, then expand as confidence and understanding grow.
9. Keep Up with AI Advancements
AI evolves rapidly. What’s cutting-edge today may be outdated tomorrow. Businesses should continuously update tools, retrain staff, and reassess workflows.
Ways to stay updated:
- Subscribe to AI newsletters or blogs
- Attend webinars and tech conferences
- Participate in AI communities for insights and best practices
Example:
Companies using generative AI for marketing should monitor new features like image-to-text or video generation to expand capabilities.
10. Encourage a Culture of AI Adoption
AI integration is not just a technical project; it’s a cultural shift. Encourage employees to experiment, provide feedback, and view AI as a partner, not a threat.
Tips:
- Recognize employees who effectively use AI
- Share success stories across teams
- Promote continuous learning and curiosity
Example:
A company might celebrate how AI-assisted analytics helped the product team identify a new market opportunity faster than manual methods, reinforcing positive adoption.
Final Thoughts
AI has the potential to transform businesses, but effective integration requires strategy, planning, and ongoing evaluation. By identifying high-impact use cases, selecting the right tools, training staff, integrating AI into workflows, and continuously monitoring performance, companies can maximize ROI while minimizing disruption.
Remember, AI is most powerful when it augments human skills, enabling employees to focus on creativity, strategy, and decision-making. With careful adoption, businesses can stay competitive, efficient, and ready for the rapidly evolving digital landscape.

