
Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools have revolutionized how we work, create, and manage tasks. From AI writing assistants and image generators to analytics platforms, these tools save time and enhance productivity. However, like any technology, AI is not perfect. Users often encounter issues ranging from inaccurate outputs to software glitches. Understanding common problems and how to troubleshoot them can help you get the most out of AI tools and avoid frustration.
This guide breaks down the most frequent AI tool issues and provides practical solutions, with real-world examples.
1. Inaccurate or Irrelevant Outputs
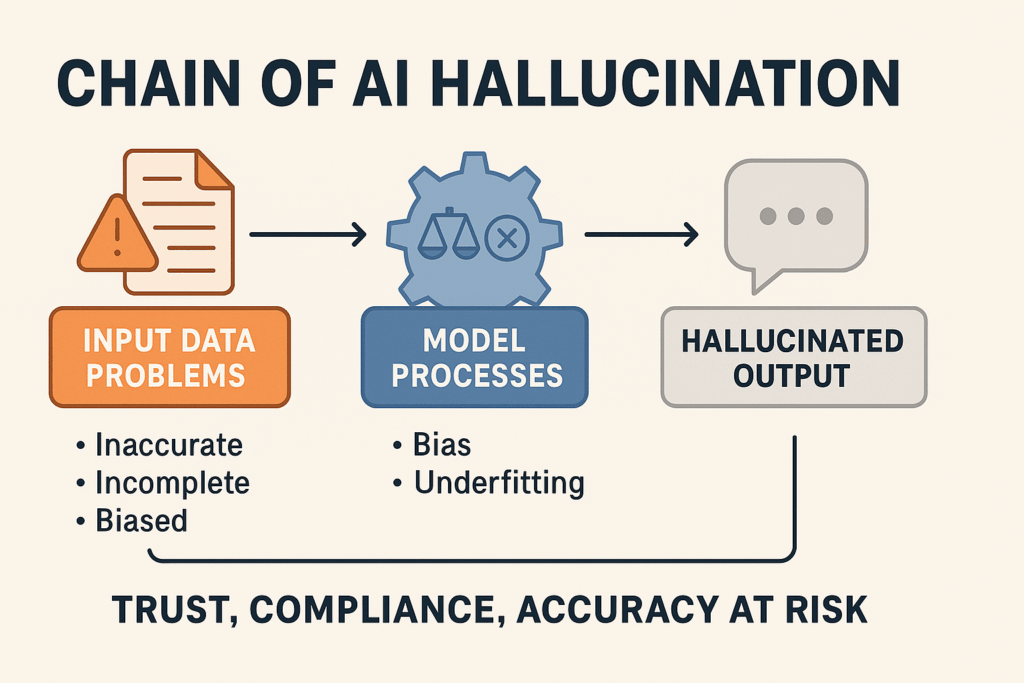
One of the most common issues with AI tools is generating results that are off-target, vague, or incorrect. This can happen with AI writing, coding, or image generation platforms.
Causes:
- Vague or poorly structured prompts
- AI misinterpreting context
- Insufficient training data for a specific niche
Troubleshooting Tips:
- Refine your prompt: Be specific about the format, style, and content.
- Example: Instead of “Write a blog post about AI,” use “Write a 300-word blog post explaining how AI helps small businesses automate social media tasks, with two examples.”
- Provide context: Include audience, tone, or scenario to guide the AI.
- Use examples: Show the AI a sample output you want it to mimic.
Pro Tip: Always review AI outputs for accuracy before publishing or using them.
2. AI Tool Freezes or Crashes
Some AI apps, especially those that handle large datasets or complex image generation, may freeze, crash, or respond slowly.
Causes:
- Insufficient system resources (RAM, CPU, GPU)
- Browser or app compatibility issues
- Large file sizes or complex requests
Troubleshooting Tips:
- Restart the app or browser: Simple, but often effective.
- Clear cache and cookies: Reduces memory load and improves performance.
- Break tasks into smaller chunks: For example, split a 10,000-word AI document request into two 5,000-word prompts.
- Check system requirements: Ensure your device meets the app’s minimum specs.
Example: AI image generators like Midjourney or DALL·E may fail with extremely detailed prompts; simplifying or splitting requests often works.
3. Output Formatting Issues
Sometimes, AI outputs text or visuals that are messy, misaligned, or unusable for your project.
Causes:
- AI not understanding the requested format
- Complex formatting (tables, code blocks, bullet points)
- Export settings or software limitations
Troubleshooting Tips:
- Specify the output format in your prompt: “Generate a table with columns for name, age, and email” or “Write in Markdown format.”
- Manually adjust formatting: Minor edits in a text editor or design software can fix alignment issues.
- Use AI for formatting fixes: Many AI tools can clean up or restructure text.
Example: If ChatGPT returns a bulleted list in plain text but you need Markdown formatting, you can prompt it: “Rewrite the list in Markdown format.”
4. AI Generates Biased or Offensive Content
AI can sometimes produce outputs that are biased, insensitive, or inappropriate, reflecting issues in its training data.
Causes:
- AI trained on biased datasets
- Ambiguous prompts that leave room for interpretation
Troubleshooting Tips:
- Review outputs carefully: Always screen AI content before use.
- Refine prompts for neutrality: Include explicit instructions like “Write in a neutral and professional tone.”
- Use moderation tools: Some AI platforms have filters to reduce offensive or biased content.
- Cross-check facts: Ensure AI suggestions are accurate and ethical.
Example: Asking AI for “examples of successful leaders” may unintentionally favor certain demographics. Clarifying “examples of diverse successful leaders from multiple industries” improves inclusivity.
5. Connectivity or Server Issues
Cloud-based AI tools often require a stable internet connection. Users may encounter errors, failed uploads, or timeouts.
Causes:
- Poor internet connection
- Server downtime or high traffic
- VPN or firewall restrictions
Troubleshooting Tips:
- Check your connection: Ensure a stable Wi-Fi or wired connection.
- Retry later: Sometimes servers experience temporary overload.
- Use a different network: VPNs or corporate firewalls can block AI services.
- Check official channels: Many AI tools post updates or maintenance schedules online.
Example: Generative AI platforms may fail during peak hours; switching to off-peak times improves performance.
6. Issues with API or Integrations
Many AI tools are integrated with other apps or platforms (e.g., AI writing in WordPress, AI analytics in Excel). Problems may arise during these integrations.
Causes:
- Incorrect API keys or credentials
- Version mismatches between software
- Rate limits on API calls
Troubleshooting Tips:
- Verify credentials and permissions: Ensure API keys are correct and active.
- Check for software updates: Compatibility issues often arise from outdated apps.
- Monitor usage limits: Some APIs restrict requests per minute or day.
- Consult documentation: Most platforms provide detailed troubleshooting guides.
Example: A Zapier integration that automatically sends AI-generated content to Slack may fail if the API token has expired.
7. AI Produces Low Creativity or Repetitive Results
AI sometimes generates outputs that feel generic, repetitive, or uninspired.
Causes:
- Repetitive prompts or limited context
- Over-reliance on default AI behavior
Troubleshooting Tips:
- Use varied prompts: Change wording, specify tone, or request alternatives.
- Ask for multiple options: “Generate three different versions of this text” often sparks creativity.
- Add constraints or style guides: “Write a humorous version in 100 words” encourages originality.
Example: If an AI repeatedly produces generic blog introductions, adding a role-based prompt like “You are a creative content marketer” often improves results.
8. Security and Privacy Concerns
AI tools handle sensitive information like emails, documents, or financial data. Mishandling or storing this data can pose risks.
Troubleshooting Tips:
- Use trusted platforms: Choose AI tools with strong privacy policies.
- Avoid sharing sensitive info unnecessarily: Replace personal data with placeholders when testing.
- Enable encryption and authentication: Secure your accounts and connections.
Example: For financial documents, use AI offline or in private environments rather than free cloud-based tools that may store data.
9. General Troubleshooting Best Practices
- Start with simple prompts or tasks: Test AI with small, clear requests before scaling up.
- Document errors and patterns: Keep a log to identify recurring issues and solutions.
- Keep software updated: Updates often fix bugs and improve AI performance.
- Reach out to support: Most AI platforms offer help guides, FAQs, and customer support.
- Experiment and iterate: AI behavior can vary; refining prompts often solves unexpected issues.
Final Thoughts
AI tools are powerful, but they are not flawless. Understanding common problems—from inaccurate outputs and formatting errors to connectivity issues and biases—helps you troubleshoot effectively and maintain productivity. By refining prompts, checking context, and following best practices, you can overcome most issues and get the best results from AI tools.
Remember, AI is a collaborative partner: it can do much of the heavy lifting, but human guidance, review, and creativity are still essential.

