3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has made incredible strides since its inception, revolutionizing how products are designed, produced, and distributed. This technology, which creates physical objects by adding material layer by layer based on a digital model, is changing industries in profound ways. From rapid prototyping to creating complex, customized products, 3D printing is reshaping manufacturing, healthcare, and even construction. In this article, we’ll explore how 3D printing is influencing various sectors and its potential to transform the future of production.
1. The Basics of 3D Printing
At its core, 3D printing is a manufacturing process that builds an object layer by layer from a digital design. The process involves creating a 3D model using computer-aided design (CAD) software, which is then fed into a 3D printer that constructs the object. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing, which removes material to create a shape, 3D printing adds material, often plastic, metal, or even bio-based substances, in layers.
Key Benefits of 3D Printing:
- Customization: 3D printing enables the creation of highly customized products, from personalized healthcare devices to unique consumer goods.
- Cost Efficiency: For low-volume production runs or prototyping, 3D printing can be much more cost-effective than traditional methods, eliminating the need for expensive molds or tooling.
- Faster Production: 3D printing drastically reduces the time from design to production, enabling quicker iterations and faster go-to-market timelines.
2. 3D Printing in Manufacturing: Revolutionizing Production
One of the most significant impacts of 3D printing has been on the manufacturing industry. Traditionally, manufacturing relied on mass production techniques like injection molding, which require large investments in molds and tooling. With 3D printing, companies can now produce complex designs more efficiently and affordably.
Key Applications in Manufacturing:
- Rapid Prototyping: One of the earliest and most widely adopted uses of 3D printing is for prototyping. Designers and engineers can quickly create functional prototypes to test and validate designs before committing to expensive and time-consuming production processes. This speeds up product development and reduces waste.
- Low-Volume and Custom Manufacturing: 3D printing enables manufacturers to produce small batches or even single, custom parts without the need for expensive tooling or molds. This is particularly useful for specialized products or spare parts that are not needed in large quantities.
- Complex Part Design: Unlike traditional methods, 3D printing can create complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using conventional manufacturing techniques. This allows companies to create stronger, lighter, and more efficient parts, especially in industries like aerospace and automotive.
Impact on Manufacturing:
- Reduced Lead Times: The ability to produce parts quickly and on-demand means that manufacturing lead times are shortened, and businesses can respond more swiftly to market changes.
- Cost Savings: Without the need for molds and tooling, production costs for small runs or customized items are significantly lower, allowing businesses to create high-quality products at lower prices.
- Supply Chain Resilience: With on-demand manufacturing capabilities, businesses can reduce their reliance on overseas production, mitigate supply chain risks, and minimize inventory costs.
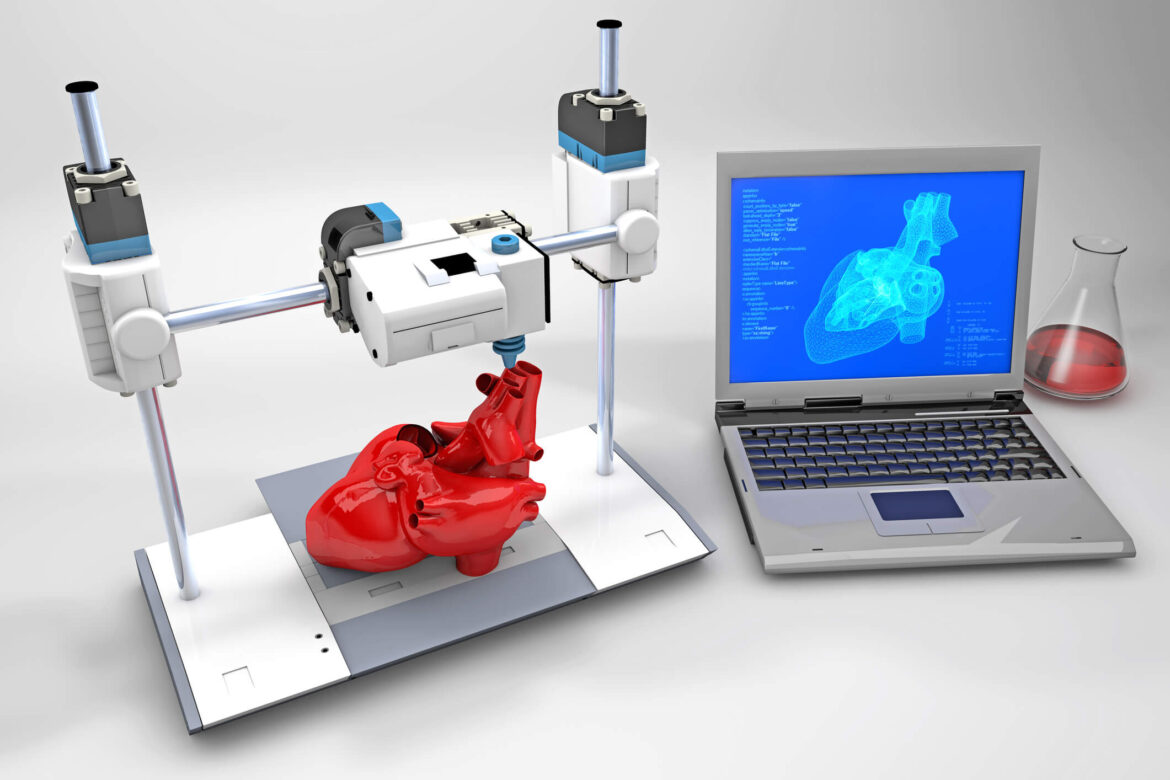
3. 3D Printing in Healthcare: Personalized Medicine and Prosthetics
3D printing has made a significant impact on the healthcare industry, where it’s being used to create personalized medical devices, prosthetics, and even tissues and organs. The ability to produce customized solutions for individual patients is one of the most promising aspects of this technology.
Key Applications in Healthcare:
- Custom Prosthetics and Implants: 3D printing enables the creation of bespoke prosthetics and implants that fit the specific measurements and needs of patients. For example, prosthetic limbs can be tailored to ensure a perfect fit, increasing comfort and functionality.
- Medical Models for Surgical Planning: Surgeons can use 3D-printed models of patients’ organs to better plan surgeries. This is particularly helpful for complex procedures, such as reconstructive surgery or heart surgeries, where understanding the patient’s anatomy in detail is crucial.
- Bioprinting: Although still in the experimental stage, bioprinting holds the potential to print tissues and organs using bio-inks made from human cells. Researchers are working on printing functional tissues, such as skin, liver, or heart tissue, for transplantation or medical research.
Impact on Healthcare:
- Improved Patient Outcomes: Personalized prosthetics and implants that are precisely tailored to a patient’s body can lead to better comfort, performance, and recovery times.
- Reduced Costs and Waiting Times: By using 3D printing, healthcare providers can produce custom implants and prosthetics on demand, reducing costs and wait times for patients who would otherwise have to wait for mass-produced models.
- Medical Research and Innovation: Bioprinting could revolutionize drug testing, organ donation, and regenerative medicine by creating tissue samples or even eventually growing organs for transplant, addressing the global shortage of donor organs.
4. 3D Printing in Construction: Building the Future
The construction industry has also begun to embrace 3D printing, with innovative companies developing large-scale printers capable of constructing buildings and structures from concrete, plastic, and even recycled materials. This technology promises to reduce construction times, lower costs, and enable the creation of more sustainable buildings.
Key Applications in Construction:
- 3D Printed Homes: Companies are already using 3D printers to construct affordable housing, with some successfully building entire homes in just a few days. These homes can be made with a combination of concrete and other materials, reducing construction costs significantly.
- Infrastructure and Urban Development: 3D printing is also being used to create bridges, roads, and other urban infrastructure. These structures can be built with less material waste and in less time than traditional methods.
- Sustainability: 3D printing in construction allows for the use of recycled materials and more energy-efficient designs, contributing to greener, more sustainable building practices.
Impact on Construction:
- Faster and Cheaper Construction: By streamlining the construction process and reducing labor costs, 3D printing can significantly lower the cost of building homes and infrastructure. It also shortens construction timelines, enabling rapid development.
- Customization and Design Flexibility: Architects and engineers can design more complex, customized buildings with intricate details that would be costly or impossible to create using traditional construction methods.
- Sustainability: 3D printing allows for more efficient use of materials and reduces waste, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional construction methods.
5. The Environmental Impact of 3D Printing
While 3D printing offers numerous benefits, such as reduced waste and the ability to produce products on demand, there are environmental concerns that need to be addressed. The materials used in 3D printing, such as plastics and metals, can have environmental impacts if not managed properly.
Key Environmental Considerations:
- Material Waste: While 3D printing is more material-efficient than traditional manufacturing, the production of parts often uses non-recyclable plastics, which can contribute to plastic pollution.
- Energy Consumption: Some 3D printing processes, especially in industrial applications, can consume a significant amount of energy, particularly when using high-temperature materials like metals.
- Sustainable Materials: The growing trend in 3D printing is toward using eco-friendly materials, including biodegradable plastics, recycled plastics, and even organic materials, to reduce environmental impact.
Impact on the Environment:
- Reduced Waste: One of the primary benefits of 3D printing is the reduction of waste. Traditional manufacturing often involves cutting away large amounts of material to shape a part, whereas 3D printing only uses the material needed for the object.
- Sustainability Innovation: The rise of sustainable materials in 3D printing can help address environmental concerns, with companies increasingly exploring ways to make the process more eco-friendly.
6. The Future of 3D Printing
The potential applications of 3D printing continue to expand across industries, and its impact is only expected to grow in the coming years. As the technology becomes more advanced, the cost of 3D printers continues to decrease, making it accessible to more businesses, and even individuals, around the world. With the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and automation, 3D printing will continue to evolve, creating new opportunities for customization, efficiency, and innovation.
Emerging Trends in 3D Printing:
- Mass Customization: 3D printing is opening up new possibilities for mass customization, allowing for highly personalized products in fields like fashion, automotive, and healthcare.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Combining AI with 3D printing can help optimize designs, predict material properties, and enhance the printing process, further improving efficiency and capabilities.
- Bioprinting and Organ Printing: Continued advancements in bioprinting could lead to breakthroughs in creating tissues and organs for medical use, providing hope for patients waiting for organ transplants.
Conclusion: A Transformative Technology
3D printing is no longer just a tool for rapid prototyping—it’s a transformative technology that’s reshaping industries from manufacturing to healthcare to construction. With its ability to create customized products, reduce costs, and accelerate production, 3D printing offers exciting possibilities for the future. While challenges like environmental impact and material limitations remain, the continuous evolution of this technology holds the potential to drive innovation and change the way we design, produce, and consume goods. As 3D printing continues to advance, its influence will only grow, making it a central force in the future of manufacturing and beyond.